Harriet Tregoning, the director of D.C.’s Office of Planning, just made some big news as far as the city’s developers, smart-growth advocates, and car owners are concerned. The long-overdue update to D.C.’s 55-year-old zoning code, which the office is currently working on, will preserve mandatory parking minimums in transit zones for new residential and commercial developments.
Harriet Tregoning, the director of D.C.’s Office of Planning, just made some big news as far as the city’s developers, smart-growth advocates, and car owners are concerned. The long-overdue update to D.C.’s 55-year-old zoning code, which the office is currently working on, will preserve mandatory parking minimums in transit zones for new residential and commercial developments.
Tregoning made the announcement during a segment on WAMU’s The Politics Hour. While D.C. has quite a large car-free population—38.5 percent of households, according to the U.S. Census Bureau—car owners have worried that the end of parking minimums at new developments would tighten the availability of on-street parking.
Developers that construct new buildings in transit zones—within a half-mile of a Metro station or quarter-mile of a busy bus stop—are required to outfit those projects with a certain number of parking spaces. Critics of the policy say the requirements drive up costs of new housing units by an average of 12.5 percent, WAMU reported earlier this month.
Instead of allowing developers to install as many or as few parking spots as they like, Tregoning said the minimums will be reduced. The Office of Planning will submit its code overhaul to the city’s Zoning Commission later this month.
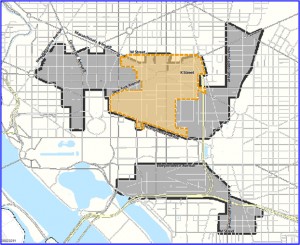
UPDATE, 5 p.m.: Tregoning adds that the elimination of parking minimums will still apply to downtown D.C., the definition of which is being expanded according to a map she sent to DCist. The area colored in orange is what current zoning laws consider to be “downtown,” but when Tregoning’s office submits its report to the zoning commission, downtown will be expanded outward to include the entire shaded area, which stretches from Dupont Circle to NoMa. The map also includes a southern swath of the city encompassing Southwest Waterfront and Navy Yard.
Even though the areas the Office of Planning include many of D.C.’s construction sites, Tregoning told Housing Complex she expects some backlash from the smart-growth advocates who would have preferred the entire city to lose its parking requirements. And sure enough, the backlash came quickly in the form of the Coalition for Smart Growth.
“We are disappointed that the opposition to progressive reforms has caused the city to back down on the important reform of removing minimum parking requirements,” Stewart Schwartz, the group’s executive director said in a statement. “The costs of too much parking are being passed on to all residents even if they want to save money by living car free. Moreover, parking requirements will still be lowered in the city’s transit zones. That’s as it should be. With the expanded transit, walking, biking, and carsharing options that DC now offers, we shouldn’t be mandating more parking than we need or than people will use.”
Photo Courtesy of Kerrin Nishimura, DCist.